What Is a Filter Plate and Frame System and Why Does It Still Matter in Modern Filtration?
Gen 10, 2026
A filter plate and frame system remains one of the most reliable and widely used solid-liquid separation technologies in industrial filtration. The short answer to why it still matters is simple: despite advances in automation and membrane technologies, the plate and frame concept offers unmatched flexibility, predictable filtration performance, and proven durability across a wide range of industries. From wastewater treatment to chemical processing, this classic filtration design continues to play a critical role in modern production lines.
In this article, we explore how filter plate and frame systems work, where they are best applied, how to choose the right configuration, and why they remain a preferred solution for industrial buyers worldwide.
How Does a Filter Plate and Frame System Work?
The filter plate and frame system operates on a straightforward yet highly effective principle. A series of alternating filter plates and frames are assembled into a press. Filter cloths are mounted on the plates, and slurry is pumped into the chambers formed between plates and frames.
As pressure builds:
- Liquid passes through the filter cloth
- Solids are retained, forming a filter cake
- Clarified filtrate exits through internal channels
This batch filtration process allows for precise control over cake thickness, filtration pressure, and cycle time. Unlike continuous filtration systems, the plate and frame design provides high solids capture efficiency and excellent filtrate clarity.
Because of its mechanical simplicity and modular structure, the filter plate and frame configuration remains a cornerstone technology in industrial filtration systems worldwide.
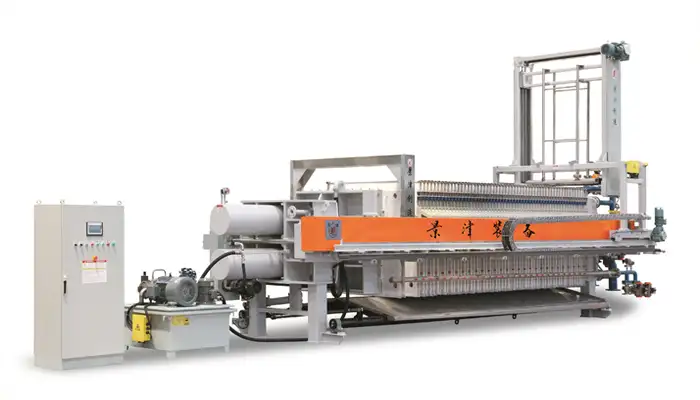

Key Components of a Filter Plate and Frame Press
Understanding the main components is essential for evaluating performance, maintenance requirements, and lifecycle cost.
The core elements include:
- Filter plates: Typically made from reinforced polypropylene, cast iron, or stainless steel
- Frames: Determine chamber depth and cake thickness
- Filter cloths: Selected based on particle size, chemical compatibility, and temperature
- Hydraulic closing system: Ensures uniform pressure sealing
- Manifold and drainage system: Collects and directs filtrate
Each component influences filtration efficiency and operational reliability. Modern designs have optimized plate geometry and sealing structures to minimize leakage and maximize effective filtration area.
This modular construction also allows the system to scale easily, making it suitable for both small pilot plants and large industrial installations.
Typical Applications Across Industries
The filter plate and frame system is valued for its adaptability across industries that require precise solid-liquid separation.
Common application sectors include:
- Municipal and industrial wastewater treatment
- Chemical and pharmaceutical processing
- Mining and mineral processing
- Food and beverage production
- Metallurgy and electroplating
In regions with strong manufacturing bases, many buyers source equipment from established suppliers of filter press china due to their experience in handling diverse sludge characteristics and high-capacity production requirements.
The versatility of the plate and frame structure allows it to process slurries with varying solids content, making it especially suitable for operations with fluctuating feed conditions.
Filter Plate and Frame vs Other Filtration Technologies
When evaluating filtration systems, industrial buyers often compare plate and frame presses with belt presses, centrifuges, or vacuum filters. Each technology has its strengths, but plate and frame systems offer distinct advantages.
Below is a comparison table highlighting key differences:
| Filtration Technology | Solids Capture | Cake Dryness | Footprint | Operational Control |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Plate and frame press | Very high | High | Medium | Excellent |
| Belt filter press | Medium | Medium | Large | Moderate |
| Centrifuge | Medium | Medium | Compact | Limited |
| Vacuum filter | Low–medium | Low | Large | Low |
The ability to achieve high cake dryness and superior filtrate clarity makes the filter plate and frame system particularly attractive for industries facing strict discharge or recycling requirements.
This is one reason why many industrial buyers still specify plate and frame designs when selecting an industrial filter press for demanding applications.
How to Select the Right Filter Plate and Frame Configuration
Selecting the correct configuration is not simply about capacity. It requires a thorough understanding of process conditions and performance goals.
Key selection factors include:
- Slurry solids concentration
- Particle size and compressibility
- Required throughput per cycle
- Target cake moisture content
- Chemical and temperature resistance
Plate size, number of plates, and frame thickness directly determine filtration area and chamber volume. For example, thicker frames allow more solids per cycle but may increase filtration time.
Advanced configurations can include membrane plates, automated plate shifting, and cloth washing systems, which further enhance efficiency while reducing manual labor.
A properly configured system delivers stable performance over years of operation, making upfront engineering evaluation essential.
Maintenance, Durability, and Operating Costs
One of the strongest advantages of the filter plate and frame system is its durability. With proper maintenance, these systems often operate reliably for decades.
Routine maintenance typically includes:
- Periodic cloth replacement
- Plate surface inspection
- Hydraulic system checks
- Seal and gasket replacement
Operating costs remain predictable because the system relies on mechanical pressure rather than high rotational speeds or complex electronics. This makes it especially attractive in regions with limited technical support resources.
For global operations, long-term availability of spare parts and standardized components is another reason buyers continue to favor plate and frame presses.
FAQ: Filter Plate and Frame Systems
Q1: What industries benefit most from filter plate and frame systems?
Industries with high solids separation requirements, such as wastewater treatment, mining, chemicals, and food processing, benefit the most.
Q2: Are filter plate and frame presses suitable for automation?
Yes. Modern systems can be equipped with automatic plate shifting, cloth washing, and PLC controls.
Q3: How does plate size affect filtration performance?
Larger plates increase filtration area and throughput but require more space and structural support.
Q4: How often do filter cloths need replacement?
Replacement frequency depends on sludge abrasiveness, chemical exposure, and operating pressure, but typically ranges from several months to years.
Q5: Can filter plate and frame systems handle corrosive materials?
Yes, with proper material selection for plates, frames, and cloths.
Why Jingjin Is a Global Leader in Filter Plate and Frame Technology
Jingjin is internationally recognized for its expertise in filter plate and frame filtration systems, offering comprehensive solutions tailored to diverse industrial needs. With advanced manufacturing capabilities, rigorous quality control, and extensive project experience, Jingjin delivers filtration equipment that meets demanding operational standards.
The jingjin filter press portfolio includes a full range of plate sizes, automation levels, and material options, supporting applications from municipal wastewater to heavy industrial sludge. Jingjin’s engineering-driven approach ensures each system is optimized for performance, durability, and lifecycle cost.
By combining innovation with proven filtration principles, Jingjin continues to support customers worldwide in achieving efficient and reliable solid-liquid separation.
References
- Wikipedia – Filter Press: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Filter_press
- Britannica – Filtration: https://www.britannica.com/technology/filtration
- Water Environment Federation (WEF) – Sludge Dewatering and Filtration
- Perry & Green, Perry’s Chemical Engineers’ Handbook, Filtration Section