Industrial Waste Water Treatment Systems: Are They the Foundation of Compliant and Profitable Manufacturing?
Feb 6, 2026
Industrial waste water treatment systems are no longer optional infrastructure. They are a foundational element of compliant, resilient, and cost-controlled manufacturing operations. For B2B decision-makers, the answer to whether these systems are worth strategic investment is clear: well-designed treatment systems protect production continuity, reduce environmental and financial risk, and increasingly determine whether a facility can operate, expand, or enter new markets. Across sectors such as chemicals, mining, food processing, metallurgy, and energy, practical examples show that modern treatment systems turn wastewater management from a regulatory burden into an operational asset.
As industrial processes grow more complex and environmental oversight tightens, wastewater treatment can no longer be addressed as a secondary utility. It must be engineered as an integrated system aligned with production goals, discharge limits, and long-term cost efficiency.

Why Industrial Waste Water Treatment Systems Are a Strategic Requirement Today
Industrial water use sits at the intersection of regulation, cost, and sustainability. This convergence has elevated wastewater treatment from a maintenance issue to a board-level concern.
Regulatory Compliance and Operational Risk
Environmental regulations increasingly limit allowable concentrations of suspended solids, heavy metals, oils, nutrients, and organic pollutants in discharged water. Non-compliance exposes manufacturers to fines, shutdowns, and reputational damage.
Industrial waste water treatment systems provide controlled, measurable removal of pollutants, allowing facilities to meet discharge permits consistently rather than reactively.
Cost Pressures and Resource Constraints
Freshwater procurement, discharge fees, and sludge disposal costs continue to rise worldwide. At the same time, water scarcity is disrupting supply reliability in many industrial regions.
Effective treatment systems reduce overall water consumption by enabling reuse and minimizing waste volumes, stabilizing operating costs over time.
Sustainability and Market Expectations
Customers, investors, and regulators increasingly expect transparent environmental performance. Robust wastewater treatment supports sustainability reporting and aligns operations with environmental, social, and governance objectives without sacrificing productivity.
Core Components of Industrial Waste Water Treatment Systems
An industrial wastewater treatment system is not a single machine but a coordinated sequence of processes designed around specific contaminants and reuse or discharge goals.
Preliminary and Primary Treatment
The first stage focuses on removing coarse solids, grit, and oils that could damage downstream equipment. Screens, grit chambers, and oil separators are commonly used here.
This stage protects system integrity rather than achieving final water quality.
Physicochemical Treatment and Solid-Liquid Separation
Most industrial pollutants are removed during physicochemical treatment, where coagulants and flocculants aggregate fine particles into removable solids.
Solid-liquid separation is the heart of this stage. Technologies such as sedimentation, flotation, and filtration are selected based on solids characteristics and performance targets.
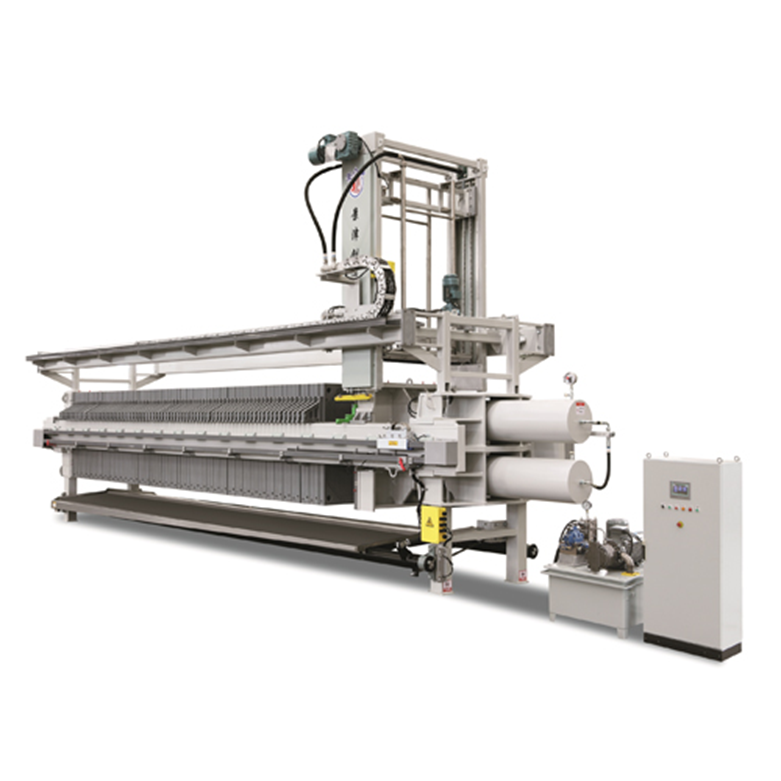
In many facilities, an industrial filter press becomes the core separation unit due to its high solids capture efficiency and ability to produce dewatered sludge with low moisture content.
Polishing and Advanced Treatment
Depending on reuse or discharge requirements, treated water may undergo further polishing through sand filtration, activated carbon, membrane systems, or disinfection.
These stages refine water quality but rely on effective upstream solids removal to operate efficiently.
The Role of Filtration in System Performance and Reliability
Filtration defines whether a treatment system delivers predictable results or struggles with variability and downtime.
High-Efficiency Solids Removal
Industrial filtration systems are designed to capture fine suspended solids that escape gravity-based processes. This improves effluent clarity and reduces loading on downstream units.
Consistent solids removal is especially critical when treated water is reused in cooling, washing, or process applications.
Sludge Volume Reduction and Handling
By producing dense, low-moisture filter cakes, filtration reduces sludge volume. This lowers transportation, disposal, or further treatment costs and simplifies waste management logistics.
System Stability Under Variable Conditions
Industrial wastewater composition often fluctuates due to production changes. Robust filtration equipment maintains performance across these variations, protecting overall system stability.
For a broader perspective on how filtration integrates into manufacturing operations, this overview of industrial filtering systems explains why filtration has become indispensable in modern industry.
Industrial Waste Water Treatment Systems Across Key Industries
Chemical and Process Manufacturing
Chemical plants generate complex wastewater containing suspended solids, dissolved organics, and reactive compounds. Treatment systems must be chemically compatible and adaptable to changing formulations.
Filter presses are commonly used to separate reaction by-products and treatment sludge reliably.
Mining and Metallurgy
Mining wastewater contains high solids loads and abrasive particles. Treatment systems prioritize robust solid-liquid separation to enable water recycling and reduce environmental discharge in remote locations.
Food and Beverage Processing
Although food industry wastewater is biodegradable, high organic loads require efficient solids removal to protect biological treatment stages and meet discharge standards.
Energy and Power Generation
Power plants rely heavily on water for cooling and flue gas treatment. Industrial waste water treatment systems allow reuse and minimize thermal and chemical pollution of receiving waters.
Performance Metrics That Guide System Design
Decision-makers evaluate treatment systems using measurable indicators that reflect both environmental and economic performance.
Table 1: Key Performance Metrics for Industrial Waste Water Treatment Systems
| Metric | Operational Significance | Business Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Suspended solids removal | Determines effluent clarity | Regulatory compliance |
| Sludge dryness | Affects disposal cost | Lower operating expenses |
| Water recovery rate | Measures reuse efficiency | Reduced freshwater intake |
| Energy consumption | Impacts lifecycle cost | Improved profitability |
| System uptime | Ensures production continuity | Reduced downtime risk |
These metrics provide a framework for comparing technologies and justifying capital investment.
Designing Systems for Long-Term Value, Not Just Compliance
A common mistake is designing treatment systems solely to meet minimum discharge limits. While compliant on paper, such systems often struggle with reliability, scalability, or operating costs.
High-performing industrial waste water treatment systems are designed with future flexibility in mind. This includes allowance for capacity expansion, tighter regulations, or increased reuse targets.
Midway through system planning, many manufacturers engage equipment specialists to validate design assumptions and lifecycle costs. For tailored system evaluation and engineering support, decision-makers can consult Jingjin directly via this contact channel.
Common Challenges and How Modern Systems Address Them
One challenge is fluctuating wastewater quality. Advanced treatment systems address this with automated dosing, robust filtration, and real-time monitoring.
Another issue is space limitation. Compact filtration equipment and modular layouts allow high treatment capacity without large footprints.
Finally, maintenance complexity can undermine system performance. Modern designs prioritize automation, easy access, and durable materials to reduce operator burden.
Frequently Asked Questions About Industrial Waste Water Treatment Systems
Are industrial treatment systems industry-specific?
Yes. While core principles are similar, system design varies significantly depending on wastewater composition, discharge limits, and reuse goals.
Can treated industrial wastewater be reused safely?
Yes, if treated to standards appropriate for the intended application. Reuse criteria are defined by process needs, not drinking water regulations.
How do filter presses improve treatment efficiency?
They achieve high solids capture and produce drier sludge, reducing downstream treatment load and disposal costs.
Is automation important in wastewater treatment systems?
Automation improves consistency, reduces human error, and lowers labor costs, especially in facilities with variable wastewater flows.
How often should systems be upgraded or reviewed?
Systems should be reviewed whenever production processes change, regulations tighten, or operating costs increase significantly.
Why Jingjin Is a Trusted Manufacturer of Industrial Waste Water Treatment Solutions
Jingjin is a globally recognized filter press manufacturer with extensive experience in industrial waste water treatment systems. Our solutions are engineered to deliver reliable solid-liquid separation, stable operation, and long-term economic value across diverse industries.
By combining robust equipment design, process expertise, and lifecycle support, Jingjin helps manufacturers meet regulatory demands while improving water efficiency and operational resilience.
References
Wikipedia, “Wastewater treatment,” https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Wastewater_treatment
Wikipedia, “Industrial wastewater treatment,” https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Industrial_wastewater_treatment
United States Environmental Protection Agency, “Industrial Wastewater,” https://www.epa.gov/eg/industrial-wastewater